Vegetation Sensitivity Index: Mapping Climate Change Risks
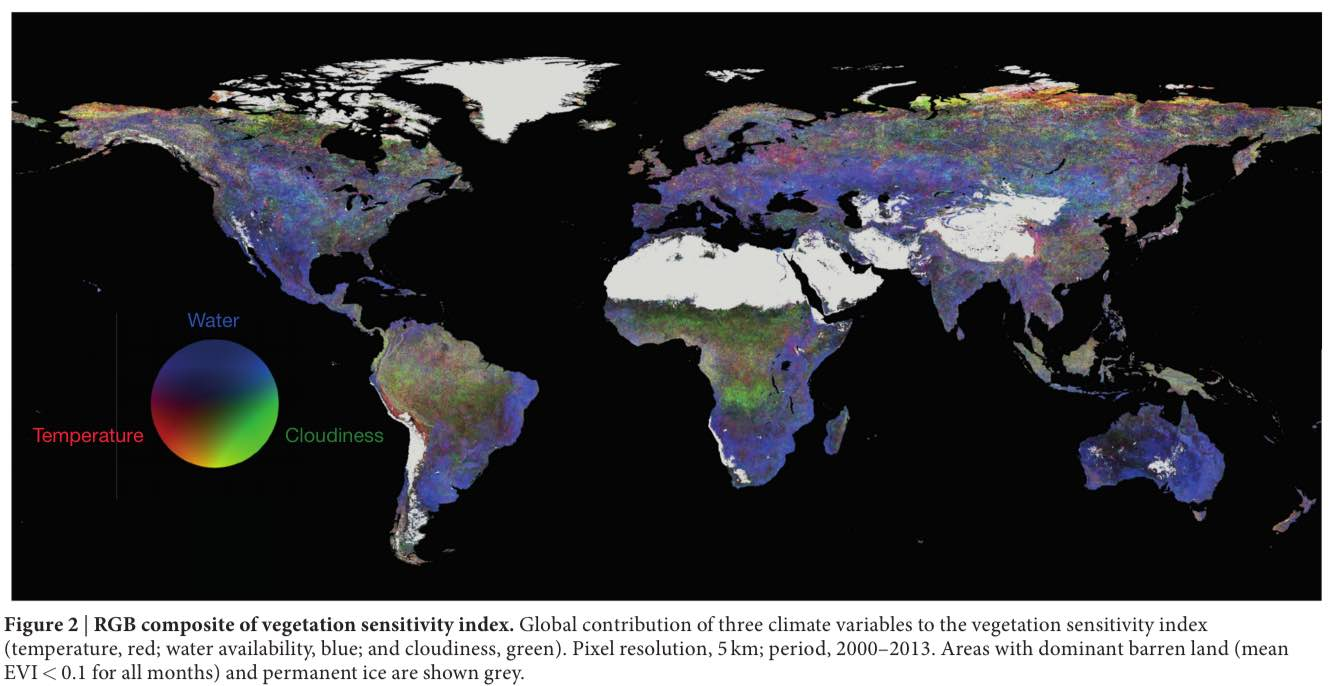
The Vegetation Sensitivity Index (VSI) is an innovative tool developed by researchers to pinpoint areas most at risk from climate change. Utilizing advanced satellite data, this index maps the most vulnerable ecosystems on Earth, effectively highlighting locations that require urgent attention due to climate variability. With climate change posing significant threats globally, understanding its impact on vegetation is crucial for sustainable management and conservation efforts. This map, published in Nature, illustrates the annual plant cover informed by satellite-based imaging, offering insights into the dynamic interplay between climate factors like temperature, water availability, and cloud cover. By identifying sensitive vegetation areas, the VSI serves as a vital resource for policymakers and conservationists aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change risks.
The concept of assessing vegetation response to environmental changes can be referred to as the vegetation resilience metric, providing insights into ecosystems under threat from shifting climatic conditions. This analytical approach, also known as ecological sensitivity evaluation, employs satellite-derived data to create detailed maps of vulnerable habitats. As we confront the pressing challenges brought on by climate fluctuations, understanding how plant communities adapt—or struggle to adapt—becomes increasingly essential. Furthermore, these vegetation mapping techniques reveal critical trends in biodiversity health, enabling better strategic planning in conservation efforts. Addressing the implications of climate instability on vital ecosystems through this lens enhances our capacity to preserve the natural world.
Understanding the Vegetation Sensitivity Index (VSI)
The Vegetation Sensitivity Index (VSI) represents a groundbreaking approach in assessing the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change. By utilizing satellite data gathered through the moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer, researchers have created a map that highlights how various regions respond to climate variability. Essentially, the VSI quantifies how much plant cover is affected by climate conditions, leading to a deeper understanding of which areas are most at risk. This innovative tool allows scientists to predict fluctuations in critical climate indicators, including temperatures, cloud cover, and moisture availability, making it invaluable for conservation efforts and climate adaptation strategies.
Moreover, the VSI is a key method for analyzing the interactions between different climate factors and vegetation health. By illustrating areas with varying responses to changing climatic conditions, researchers can identify ecosystems that may require targeted interventions to bolster their resilience. For instance, areas impacted by extreme weather events, such as droughts or floods, can be monitored more closely to assess how sustainable practices can be implemented and to evaluate the effectiveness of current conservation policies. Overall, the VSI stands out as a vital resource for climate researchers and policymakers alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the vegetation sensitivity index and how does it relate to climate change risks?
The vegetation sensitivity index (VSI) is a tool developed by researchers to assess the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change risks. It uses satellite data to map areas that are most affected by fluctuating climate variables, such as temperature and moisture levels. This index helps in identifying regions where ecological sensitivity is high due to climate variability, allowing for targeted conservation efforts.
How does satellite data contribute to the vegetation sensitivity index map?
Satellite data is crucial for creating the vegetation sensitivity index map as it provides real-time, moderate-resolution imaging of Earth’s surface. This data helps researchers monitor annual plant cover and identify how various climate change factors impact vulnerable ecosystems. By analyzing this information, the VSI can predict future changes in vegetation health related to climate variability.
What areas are identified as vulnerable ecosystems in the vegetation sensitivity index?
The vegetation sensitivity index highlights several ecologically sensitive regions that show a heightened response to climate change. Key areas include the Arctic tundra, boreal forests, tropical rainforests, and various alpine regions globally. In both North and South America, as well as parts of Australia and Asia, these regions face significant climate change risks, thus requiring urgent attention.
What role does climate variability play in determining the vegetation sensitivity index?
Climate variability is a significant factor in the vegetation sensitivity index as it influences ecosystem resilience. Changes in temperature, cloud cover, and water availability, all measured through satellite data, are critical in assessing how plant cover reacts to shifting climate patterns. These insights are essential for understanding and mitigating the risks associated with climate change.
How can the vegetation sensitivity index help in understanding future climate change impacts?
The vegetation sensitivity index serves as an analytical framework to predict how ecosystems might react to future climate fluctuations. By examining data trends regarding critical factors such as temperature and moisture, researchers can assess the health of ecosystems and develop strategies to address potential climate change impacts, particularly in vulnerable areas.
Where can I find more information about the vegetation sensitivity index and its findings?
More detailed information about the vegetation sensitivity index and its implications can be found in the publication available in Nature. This source elaborates on the methodology, findings, and significance of the VSI in relation to climate change risks, providing a comprehensive overview of the research conducted.
| Climate Variable | Color Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Red | Indicates areas sensitive to temperature changes. |
| Water availability | Blue | Signifies regions vulnerable to fluctuations in water supply. |
| Cloudiness | Green | Highlights areas impacted by changes in cloud cover. |
| Vulnerable Regions | ||
Summary
The vegetation sensitivity index (VSI) is a crucial tool in identifying areas most at risk from climate change. By mapping sensitive ecosystems using satellite data, researchers can focus on regions that need immediate attention to mitigate the impacts of global warming. This innovative approach not only showcases vulnerable ecosystems but also aids in predicting future environmental changes, making it essential for conservation efforts and policy-making.