COVID-19 Vaccine Trial: UK Government Approves Human Challenge
The COVID-19 vaccine trial represents a groundbreaking approach to accelerating the vaccine development process during a critical moment in public health. Approved by the UK Government, this pioneering initiative will utilize a human challenge trial methodology, where volunteers are intentionally infected with the Coronavirus to test vaccine efficacy. Researchers at institutions like Imperial College London are at the forefront of this effort, collaborating with renowned entities like hVIVO and the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust. As part of the trial, COVID-19 testing volunteers, aged between 18 and 30, will participate in a phased approach to determine the minimal viral dose needed for infection. With an investment of £33.6 million from the government, results expected by May 2021 could significantly reshape our understanding of vaccine development and expedite the fight against the ongoing pandemic.
The future of vaccine research is being shaped through innovative trials focusing on the COVID-19 virus, particularly through unique study designs where participants are deliberately exposed to the pathogen. Known as human challenge trials, this strategy aims to streamline the assessment of vaccine safety and effectiveness, especially under the auspices of the UK Government’s COVID vaccine program. Institutions such as Imperial College London are leading these efforts, enlisting young volunteers willing to contribute to the vital research process. This initiative could play a crucial role in informing the broader medical community about potential vaccination strategies, while also addressing ethical debates surrounding the approach. As we explore alternatives to traditional clinical trials, the collective goal remains the same: to develop robust vaccines that can combat the COVID-19 pandemic effectively.
Understanding the COVID-19 Vaccine Trial Process
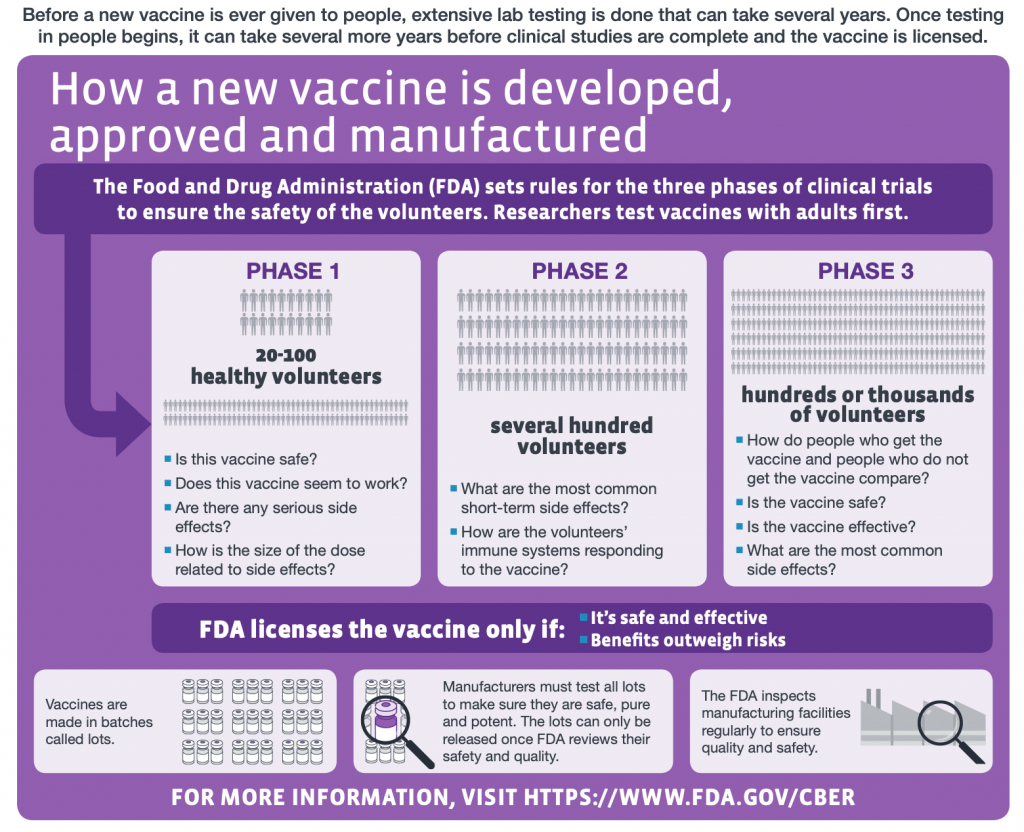
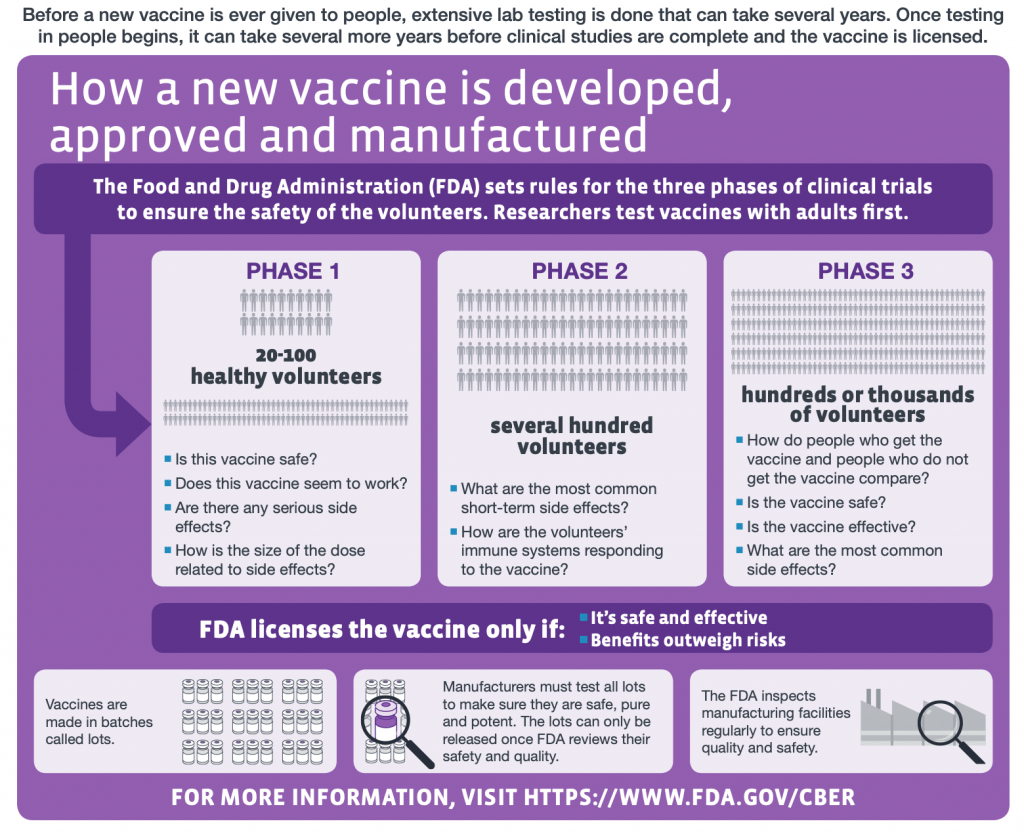
The COVID-19 vaccine trial process is a critical component in the fight against the pandemic. It involves rigorous testing phases to ensure that the vaccines are both safe and effective for human use. The trials typically begin with preclinical studies and then move to several human phases, including large-scale trials where thousands of volunteers are required. For this particular COVID-19 vaccine trial approved by the UK Government, the focus is on a human challenge trial, meaning that healthy volunteers will be intentionally infected with the virus to test the efficacy of the vaccines under conditions that closely mimic real-life exposure.
Human challenge trials like the one endorsed for COVID-19 are designed to accelerate the vaccine development process. In this trial, researchers will gather data to quickly determine how well the vaccine works against the virus. The collaboration with institutions such as Imperial College London and NHS Trusts ensures a comprehensive approach, collecting valuable insights while balancing ethical considerations amid the pandemic. In this trial, volunteers aged 18-30 will be compensated for their participation, facilitating an ample pool of data that can be analyzed for positive outcomes.
The Role of Human Challenge Trials in Vaccine Development
Human challenge trials represent a significant innovation in medical research, especially in response to pandemics like COVID-19. By allowing researchers to intentionally expose volunteers to the virus, these trials provide critical insights into the pandemic’s behavior and assess the vaccine’s effectiveness more swiftly. The UK’s approach to initiating this COVID-19 vaccine trial underscores a commitment to exploring various methodologies to combat the virus, especially given the urgency of finding effective treatments and preventive measures.
Moreover, the ethical implications of conducting human challenge trials have sparked debate among scientists and health professionals. Proponents argue that, with proper consent and strict safety protocols, these tests can lead to expedited vaccine development and can provide greater clarity on immunological responses. The collaboration with established institutions such as hVIVO and Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust highlights the importance of structured oversight. Ultimately, the success of this trial could pave the way for future studies that leverage similar methodologies in the realm of vaccine development.
Challenges and Controversies of COVID-19 Testing Volunteers
Recruiting COVID-19 testing volunteers for trials such as the one recently greenlit by the UK Government involves facing multiple ethical and logistical challenges. Since the trial requires participants to be intentionally infected with the Coronavirus, participants must be fully aware of the risks involved. This raises questions about the recruitment process and whether individuals can genuinely consent. Despite these challenges, many young adults have expressed interest in participating, driven by the desire to contribute to a solution and possibly receive compensation.
Furthermore, while these trials can accelerate the development of effective vaccines, they are not without controversy. Some members of the public and health professionals may feel uneasy about exposing participants to a virus that has caused widespread illness and death. Critics argue that human challenge trials should be reserved for diseases with fewer unknowns, where the risks are lower. Balancing public safety, ethical considerations, and scientific advancement will be crucial as these trials proceed.
Imperial College London’s Contribution to Vaccine Research
Imperial College London is at the forefront of COVID-19 research, specifically in vaccine development. Their involvement in the UK Government’s human challenge trial underscores their commitment to rapidly advancing solutions against COVID-19. As a prestigious institution, Imperial brings together a cadre of researchers and clinicians who are leveraging existing knowledge and technologies to develop a strong vaccine candidate. By utilizing human challenge trials, the college aims to contribute significantly to understanding how quickly we can craft effective vaccines.
The collaboration with other organizations, such as hVIVO and the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, strengthens the capability to safely conduct these complex trials. The expertise of researchers at Imperial College ensures that each phase of the trial is conducted rigorously, incorporating findings from previous pandemic responses and adjusting methodologies accordingly. As the trial progresses, Imperial College aims to deliver not only crucial data regarding vaccine effectiveness but also insights that can inform global health policy decisions going forward.
Funding and Support for the COVID-19 Vaccine Program
The UK Government’s allocation of £33.6 million to the COVID-19 vaccine program highlights the seriousness of the ongoing pandemic and the urgency of finding effective vaccine solutions. This significant funding is intended to support various aspects of vaccine development, including the human challenge trial. Through this financial support, researchers will be able to conduct more extensive testing, raise awareness among potential volunteers, and improve public engagement regarding vaccine efficacy and safety.
The involvement of governmental funding also reflects a broader commitment to public health, showcasing a proactive approach to addressing COVID-19. With the right investments, particularly in innovative trial designs such as human challenge studies, governments can help expedite the vaccine development process while ensuring that ethical standards are upheld. The challenge trial is a crucial component of a larger strategy that aims not just to solve the immediate crises but also to prepare for future health emergencies.
The Timeline for COVID-19 Vaccine Development
Establishing a timeline for the COVID-19 vaccine development process is essential for managing public expectations and ensuring a structured approach to research. The initial phases of testing are often lengthy and rigorous, involving preclinical studies and later moving to human trials. For the COVID-19 challenge trial set to start in January 2021, researchers expect to begin analyzing results around May 2021, marking a significant forward step in understanding the vaccine’s potential efficacy.
This important timeline serves as both a beacon of hope and a reminder of the work that still lies ahead. If successful, the velocities at which results are obtained could redefine the pace of vaccine development, guiding future approaches to public health and emergency preparedness. Researchers are hopeful that this timeline will serve as a model for tackling similar global health crises in the future.
Safety Protocols in the COVID-19 Human Challenge Trial
Safety is paramount in any clinical trial, but particularly in human challenge trials where participants are deliberately exposed to a virus. The UK Government’s COVID-19 vaccine trial follows stringent protocols to ensure that all aspects of participant safety are considered and addressed. The oversight from seasoned researchers and the ethics committee ensures that potential risks, like severe illness from COVID-19, are mitigated through informed consent and safety monitoring throughout the trial.
Additionally, participants are provided with comprehensive medical support to monitor their health and manage any reactions that arise from infection. The commitment to transparency and participant well-being reinforces public trust in vaccine research, which is crucial for wider adoption once a safe and effective COVID-19 vaccine is developed. As the trial progresses, continual assessment of safety measures will be implemented to adapt to findings and refine protocols.
Impact of Public Perception on Vaccine Trials
Public perception plays a significant role in the acceptance and success of COVID-19 vaccine trials. The approach taken by the UK Government to implement human challenge trials has received mixed reactions from various segments of society. Some express enthusiasm for speeding up the vaccine development process, while others voice concerns about the safety and ethics of intentionally infecting volunteers. Understanding and addressing these perceptions is critical to ensure robust participation and support for the trials.
Moreover, clear communication from researchers and officials about the purpose and processes of these human challenge trials can help alleviate fears. By emphasizing the stringent safety measures and the potential benefits of successful vaccine outcomes, stakeholders can foster a more informed and supportive public environment. The interaction between scientists, policy makers, and the public will be essential in shaping the future of vaccine research and overall public health strategies.
Future of Vaccine Development Beyond COVID-19
The lessons learned from the COVID-19 vaccine trials, particularly those involving human challenge methods, may reshape the landscape of vaccine development well beyond this pandemic. As researchers gather significant data on the efficacy and safety of vaccines, protocols established during this time could serve as templates for addressing future infectious disease outbreaks. Public health agencies may consider adopting similar fast-tracked trial methodologies to bring vaccines to the public more swiftly.
Furthermore, there is an opportunity for collaboration across borders, enabling a collective effort in vaccine research and development. The ongoing innovations in trial designs and the integration of technology in monitoring participant health pave the way for a transformative approach in global health. By prioritizing rapid response mechanisms and adaptive methodologies, the international community can enhance preparedness for future pandemics, ensuring that effective vaccines are at hand when needed the most.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the UK Government COVID vaccine trial and how does it work?
The UK Government COVID vaccine trial is a ‘human challenge trial’ that involves intentionally infecting volunteers with the Coronavirus to study the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. This process, approved on October 20, 2020, includes a collaboration with experts from Imperial College London and aims to accelerate vaccine development by gathering critical data.
How does a human challenge trial differ from traditional COVID-19 vaccine trials?
A human challenge trial differs from traditional COVID-19 vaccine trials by intentionally exposing vaccinated volunteers to the virus, allowing researchers to observe the immune response more quickly. While typical trials rely on natural infection rates over time, challenge trials can provide faster insights into vaccine effectiveness and safety.
Who can participate in the COVID-19 vaccine trial conducted by Imperial College London?
Participants in the COVID-19 vaccine trial conducted by Imperial College London are paid volunteers aged 18 to 30. They will be involved in the trial to help determine the minimum infectious dose of the Coronavirus and assess the vaccine’s effectiveness against the virus.
What is the timeline for results from the COVID-19 vaccine trial?
The COVID-19 vaccine trial is scheduled to begin in January 2021, pending ethics approval, with results expected by May 2021. This timeline is crucial for expediting the vaccine development process amidst the ongoing pandemic.
What ethical considerations are involved in the UK Government COVID vaccine trial?
The UK Government COVID vaccine trial raises ethical considerations primarily around the exposure of healthy volunteers to the Coronavirus. The ethics committee is tasked with ensuring that the potential benefits of the trial justify the risks to participants, alongside strict safety protocols to protect their health.
How will the UK Government fund the COVID-19 vaccine trials?
The UK Government will support the COVID-19 vaccine trials with £33.6 million (approximately $43.5 million), directed towards the operational costs of conducting the trials and ensuring the safety of participating volunteers.
What role does hVIVO play in the COVID-19 vaccine trial?
hVIVO is involved in the UK Government COVID vaccine trial by providing expertise in conducting human challenge trials. They collaborate with the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust to ensure the trial adheres to rigorous safety and ethical standards.
What are the benefits of conducting COVID-19 testing volunteers in a challenge trial?
Conducting COVID-19 testing volunteers in a challenge trial allows researchers to gather vital data more rapidly compared to conventional trials. This accelerated process can lead to quicker identification of effective vaccines and treatments for COVID-19, potentially reducing the pandemic’s impact.
Will the COVID-19 vaccine trial include diverse populations?
The current focus of the COVID-19 vaccine trial is on volunteers aged 18 to 30, which may limit diversity. Future phases of the vaccine development process will aim to include a broader demographic to ensure the vaccine’s effectiveness across different populations.
What are the risks associated with the COVID-19 human challenge trial?
The primary risks associated with the COVID-19 human challenge trial include the possibility of severe illness or complications from the virus. However, strict protocols, safety measures, and close monitoring by expert teams aim to minimize these risks for volunteer participants.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Trial Approval | The UK Government approved a COVID-19 vaccine trial on October 20, 2020. |
| Trial Type | This trial is a ‘human challenge trial’ where volunteers will be intentionally infected with the virus. |
| Funding | The trial will be funded with £33.6 million (approximately $43.5 million) from the UK Government. |
| Trial Partners | Conducted by hVIVO and the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust. |
| Volunteer Age Group | Paid volunteers aged between 18 and 30 will participate. |
| Trial Phases | Phase one will determine the minimum dose of the virus required for infection. |
| Public Opinion | While some oppose the trial due to the risks associated with COVID-19, others support it to expedite vaccine development. |
| Expert Commentary | Peter Openshaw emphasizes the importance of rapid and effective vaccine development through such trials. |
Summary
The COVID-19 vaccine trial approved by the UK Government marks a critical step in the race to develop effective vaccines against the pandemic. Initiated on October 20, 2020, this unprecedented human challenge trial will involve intentionally infecting volunteers in a controlled environment to ascertain the efficacy of potential vaccines. By strategically funding and orchestrating this trial, the UK aims to accelerate the vaccine development process. It represents a bold move amidst public concern, as participants will be carefully monitored, ensuring scientific validity while exploring new methods to tackle COVID-19. As results become available in mid-2021, they will be pivotal in assessing the balance of risk and reward in this innovative approach.